What Is Personal Information And Why Is It Valuable
페이지 정보
작성자 Lamont 댓글 0건 조회 31회 작성일 24-08-15 12:56본문
In the digital age, the safeguarding of certain types of data has become paramount. This section delves into the significance of protecting sensitive details that individuals share online, exploring how such measures contribute to overall security in the digital realm.
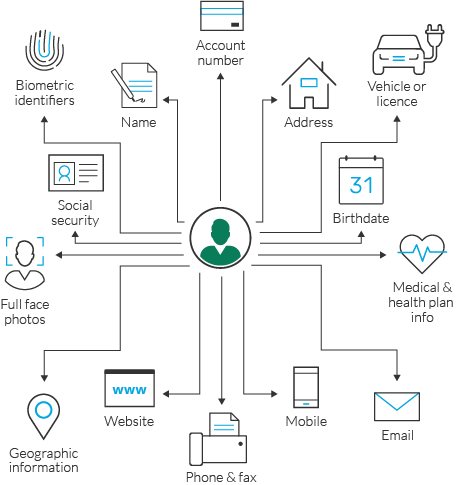
Sensitive Data encompasses a variety of elements that can include names, addresses, financial details, and more. The value of such data lies in its potential use, both legally and illicitly. Understanding the mechanisms by which this data is protected and exploited is crucial for maintaining a secure digital environment.
Cybersecurity measures are continually evolving to meet the challenges posed by increasingly sophisticated threats. These measures are designed to shield sensitive data from unauthorized access and misuse. The implications of inadequate protection can be far-reaching, affecting not only personal privacy but also the integrity of financial systems and the stability of online interactions.
Defining the Scope of Personal Data

This section delves into the intricacies of categorizing and understanding the breadth of data that pertains to individuals. It is crucial to delineate the boundaries of such data to ensure proper protection and ethical handling. The scope encompasses a wide array of data types, each carrying varying levels of sensitivity and implications for the individuals involved.
| Type of Data | Description | Sensitivity Level |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Identifiers | Includes names, addresses, and contact details. | Low to Medium |
| Financial Details | Bank account numbers, credit card details, and transaction histories. | High |
| Health Records | Medical histories, diagnoses, and treatment details. | Very High |
| Behavioral Data | Data collected from online activities, preferences, and habits. | Medium to High |
| Biometric Data | Fingerprints, facial recognition data, and other unique biological identifiers. | Very High |
Each category of data listed above requires specific considerations in terms of storage, access, and usage. The sensitivity level indicates the potential harm that could result from unauthorized access or misuse, guiding the necessary security measures and legal protections. Understanding the scope of such data is essential for implementing effective strategies to safeguard individual rights and privacy.
Defining the Scope of Personal Data
In this section, we delve into the intricate landscape of data protection, focusing on the boundaries that define sensitive data. The evolution of privacy concerns is a pivotal aspect in understanding how societal norms and technological advancements shape our perception and protection of individual details.
Historically, the concept of privacy was relatively straightforward, often limited to physical spaces and personal correspondence. However, with the advent of digital technology, the scope of what constitutes sensitive data has expanded dramatically. Today, it encompasses a wide array of digital footprints, including browsing history, purchase records, and even biometric data.
The shift towards a more interconnected world has inevitably led to an increase in the types of data that are considered private. This expansion is not merely quantitative but also qualitative, as new forms of data emerge with the development of technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things.
Moreover, the legal frameworks that govern data protection are continually evolving to meet these new challenges. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe exemplify a comprehensive approach to defining and protecting sensitive data. These frameworks aim to balance the rights of individuals to protect their personal details with the needs of businesses and governments to collect and analyze data for various purposes.
Understanding the scope of sensitive data is crucial for both individuals and organizations. For individuals, it empowers them to make informed decisions about their digital footprint. For organizations, it guides ethical data collection practices and compliance with legal standards, thereby mitigating potential legal and reputational risks.
In conclusion, the definition of what constitutes sensitive data is dynamic and influenced by technological, legal, and societal changes. As we continue to navigate this evolving landscape, it is essential to maintain a vigilant and informed approach to data protection.
The Evolution of Privacy Concerns
Over the years, the apprehension surrounding individual confidentiality has significantly transformed. This section delves into the historical progression of these anxieties, exploring how societal and technological advancements have reshaped our understanding and expectations of seclusion.
Historical Context: Initially, concerns about confidentiality were primarily focused on physical documents and personal interactions. However, with the advent of digital technology, the landscape dramatically shifted. The proliferation of online platforms and the storage of sensitive details in digital formats introduced new vulnerabilities and sparked a heightened awareness of potential breaches.
Technological Impact: The rapid evolution of the internet and communication tools has not only made it easier to share and access vast amounts of data but also made it more challenging to protect. The emergence of sophisticated hacking techniques and data mining practices has further escalated these concerns, leading to a continuous adaptation of security measures and legal frameworks.
Societal Awareness: As incidents of data leaks and unauthorized access became more prevalent, public consciousness about the importance of safeguarding personal details grew. This increased awareness has driven both individuals and organizations to seek more robust methods of protection, influencing the development of privacy laws and ethical standards in data handling.
Future Outlook: Looking ahead, the trajectory of privacy concerns is likely to continue evolving in response to technological innovations and societal shifts. As we navigate this dynamic environment, ongoing education and proactive strategies will be crucial in maintaining a balance between convenience and security.
The Value of Personal Information

In this section, we delve into the economic dynamics surrounding the exchange of sensitive data. The focus is on how such data is not merely a byproduct of modern digital interactions but a commodity with significant market value.
Economic Aspects of Data Trading
The trade of sensitive data has become a lucrative sector in the global economy. This trade encompasses a wide array of data types, from basic demographic details to more intricate behavioral patterns. The value of such data lies in its ability to provide insights that can influence business strategies, marketing campaigns, and even political outcomes.
Organizations are willing to invest heavily in acquiring this data due to its potential to enhance decision-making processes and increase profitability. For instance, consumer behavior data can help companies tailor their products and services to better meet the needs of their target audiences, thereby boosting sales and customer satisfaction.
Moreover, the advent of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence has further amplified the value of this data. These technologies enable the extraction of complex patterns and predictions from large datasets, which can be pivotal in gaining a competitive edge in various industries.
However, this economic activity raises significant ethical and legal questions. The collection and use of such data must be balanced with the rights and interests of the individuals from whom the data is sourced. This balance is crucial in maintaining trust and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
In conclusion, the economic aspects of data trading underscore the critical role that sensitive data plays in contemporary business and economic strategies. Understanding these dynamics is essential for both businesses and consumers in navigating the complexities of the digital age.
Economic Aspects of Data Trading
This section delves into the intricate dynamics of data commerce, exploring how the exchange of sensitive details impacts global economic structures. The focus here is on understanding the mechanisms through which data transactions influence market strategies and financial outcomes.
Data trading has become a cornerstone in the modern economic landscape. It involves the buying and selling of detailed records, which can range from consumer habits to financial transactions. The economic implications of these activities are profound, affecting not only the profitability of businesses but also the stability of financial markets.
- Market Expansion: The availability of detailed records enables companies to expand their market reach by targeting specific demographics more effectively.
- Cost Efficiency: Data-driven strategies often lead to more efficient resource allocation, reducing operational costs and enhancing profitability.
- Innovation Catalyst: The insights gained from data trading spur innovation, leading to the development of new products and services tailored to consumer needs.
However, the economic benefits of data trading are not without challenges. The ethical and legal considerations surrounding the use of sensitive records are significant. Regulators worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing data practices to ensure consumer protection and fair market practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Companies must navigate complex regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance with data protection laws, which can impact operational costs and market strategies.
- Consumer Trust: The misuse of sensitive records can erode consumer trust, leading to reputational damage and potential loss of business.
- Market Transparency: Ensuring transparency in data transactions is crucial for maintaining a fair and competitive market environment.
In conclusion, while data trading offers substantial economic advantages, it also presents significant challenges that require careful management. Balancing the pursuit of economic gains with ethical considerations and regulatory compliance is essential for sustainable growth in the data-driven economy.
Strategic Importance in Cybersecurity
In the realm of digital defense, the strategic implications of data protection extend far beyond mere security measures. This section delves into how safeguarding sensitive data is crucial not only for individual safety but also for broader strategic objectives within the digital landscape. The focus here is on understanding the multifaceted roles that data protection plays in maintaining overall cybersecurity posture.
Data protection is a cornerstone of effective cybersecurity strategies. It involves not just the prevention of unauthorized access, but also the strategic management of data to ensure its integrity and availability. This is particularly vital in an era where digital assets are integral to both personal and corporate operations.
| Aspect | Importance | Strategic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Prevention of Data Theft | Critical for maintaining trust and operational continuity | Enhances reputation and reduces potential legal liabilities |
| Data Integrity | Ensures the accuracy and consistency of data over its lifecycle | Supports decision-making processes and regulatory compliance |
| Data Availability | Ensures data is accessible when needed | Aids in uninterrupted business operations and service delivery |
Understanding these elements is essential for crafting comprehensive cybersecurity strategies. Each aspect contributes uniquely to the overall resilience of an organization against cyber threats. By prioritizing data protection, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance their operational capabilities, and maintain a competitive edge in the digital marketplace.
In conclusion, the strategic importance of data protection in cybersecurity cannot be overstated. It is a multifaceted endeavor that requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the digital assets of individuals and organizations are secure and effectively managed.
Risks Associated with Data Exposure
In this section, we delve into the various perils that individuals face when their sensitive details are exposed to unauthorized entities. The consequences of such exposure can range from minor inconveniences to severe disruptions in one's life, affecting financial stability, reputation, and personal safety.
Data breaches and unauthorized access to private details have become increasingly common in today's digital age. Understanding the specific threats associated with such exposure is crucial for implementing effective protective measures. Below is a table summarizing the most prevalent risks:
| Type of Risk | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Identity Theft | Unauthorized use of an individual's personal details to commit fraud or other illegal activities. | Financial loss, legal issues, and long-term damage to credit history. |
| Financial Fraud | Illegal access to financial accounts or misuse of financial information. | Immediate financial loss and potential long-term financial instability. |
| Reputational Damage | Negative impact on an individual's reputation due to the public exposure of sensitive or opt out white pages embarrassing details. | Social ostracism, loss of employment opportunities, and personal distress. |
| Cyberstalking | Persistent online harassment or surveillance by an individual or group. | Psychological distress, fear for personal safety, and disruption of daily life. |
| Data Manipulation | Alteration of personal data by unauthorized parties, potentially leading to incorrect information being used in critical decisions. | Misrepresentation in legal, financial, or personal contexts, leading to incorrect judgments or actions. |
Each of these risks highlights the importance of safeguarding sensitive data. Implementing robust security measures and being vigilant about the handling of personal details can significantly mitigate these threats. It is essential for individuals and organizations alike to recognize the severity of these risks and take proactive steps to protect against them.
Common Threats to Personal Privacy
This section delves into the various challenges that undermine the confidentiality of individual details. As technology advances, so do the methods employed by those seeking unauthorized access to sensitive data. Understanding these threats is crucial for implementing effective safeguards.
| Type of Threat | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing Attacks | Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive details by disguising as a trustworthy entity in electronic communications. | Can lead to unauthorized access and financial loss. |
| Malware Infections | Software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system. | Can result in data theft or system corruption. |
| Data Breaches | Incidents where sensitive, protected, or confidential data is copied, transmitted, viewed, stolen, or used by an individual unauthorized to do so. | Can severely compromise personal security and privacy. |
| Spyware | Software that aims to gather information about a person or organization without their knowledge and transmits that data to another entity in a way that harms the user. | Can lead to significant privacy invasions and misuse of personal data. |
| Unsecured Networks | Networks that lack proper security measures, making them vulnerable to interception of data. | Can expose personal communications and transactions to eavesdroppers. |
Each of these threats poses a unique risk to the integrity of personal data. Awareness and proactive measures are essential to mitigate these risks and protect the confidentiality of one's private details.
Impact of Data Breaches on Individuals
In this section, we delve into the profound repercussions that unauthorized access to sensitive details can have on affected persons. The consequences are multifaceted, affecting not only the immediate security of the individuals but also their emotional well-being and financial stability.
Financial Ramifications: One of the most direct impacts is the financial loss. When unauthorized parties gain access to banking or credit card details, the potential for fraudulent transactions is high. This can lead to immediate monetary loss and long-term credit damage, complicating future financial transactions and potentially leading to bankruptcy in severe cases.
Emotional and Psychological Effects: Beyond the financial implications, there are significant emotional and psychological tolls. Victims often experience stress, anxiety, and a pervasive sense of vulnerability. The violation of personal space and the fear of future incidents can lead to chronic anxiety and even depression.
Reputational Damage: In some instances, particularly those involving social media or professional networks, the exposure of sensitive data can lead to reputational harm. This can affect both personal relationships and professional opportunities, as trust is eroded and opportunities are lost due to perceived negligence or compromised integrity.
Legal Implications: There may also be legal consequences for individuals whose data has been compromised. This can range from the need to prove innocence in cases of identity theft to facing legal penalties if the data breach involves compliance failures with industry regulations.
In conclusion, the impact of such breaches extends far beyond the immediate aftermath, affecting various aspects of an individual's life. It is crucial for both individuals and organizations to understand these risks and implement robust measures to prevent such incidents and mitigate their effects when they occur.
- 이전글Seven Trendy Ideas For your Learn More About Sewer Repair 24.08.15
- 다음글Elite Plumbing Services in Los Angeles 24.08.15
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.